Ribose has a hydroxyl group at the 2 carbon unlike deoxyribose which has only a hydrogen atom. Adenine and guanine are purines cytosine and uracil are pyrimidinesA phosphate group is attached to the 3 position of one ribose and the 5 position of the next.
How Do Dna And Rna Nucleotides Differ Socratic
RNA shares a similar structure to DNA except it contains only one strand rather than two so.
. DNA and RNA A nucleotide is made up of three components. DNA forms a. A five-carbon sugar molecule a nucleobasethe two of which together are called a nucleosideand one phosphate groupWith all three joined a nucleotide is also termed a nucleoside monophosphate nucleoside diphosphate or nucleoside triphosphate depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate group.
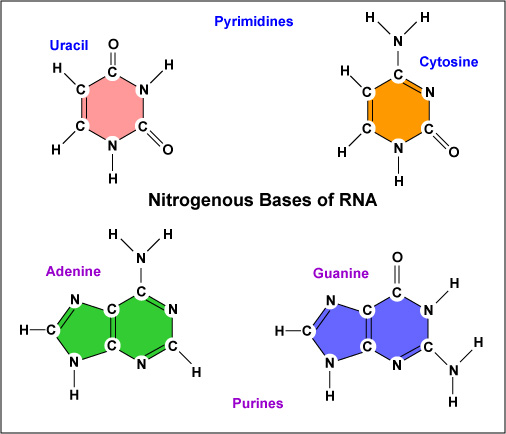
A back bone of. Uracil is one of the four nitrogenous bases in RNA molecule that is represented by the letter U. They are found in all organisms.
Although RNA is typically single stranded within cells there is significant diversity in viruses. The base is attached to the 1 position of the ribose and the. DNA is made of four types of nucleotide.
While three of their four nitrogenous bases are the same RNA molecules the have a base called uracil U instead of a thymine base. Figure 95 The difference between the ribose found in RNA. 1 nitrogenous base Nitrogenous bases are divided into two complementary groups.
RNA was first genetic material. Rhinoviruses which cause the common cold. Its a pyrimidine and has a large single ring structure.
There are five different molecules that can make up nitrogenous bases on nucleotides. Because the cell is very small and because organisms have many DNA molecules per cell each DNA molecule must be tightly packaged. In the case of RNA the five-carbon sugar is ribose not deoxyribose.
However there are some key differences between DNA and RNA molecules. RNA has ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases A G C and uracil U. The structure of RNA nucleotides are also similar to those of DNA.
Two examples of nucleic acids include. FAD NAD in the. The bases connect in the middle.
Each base has what is known as a complementary base that it binds to exclusively to form DNA and RNA. During DNA replication DNA unwinds so it can be copied. This packaged form of the DNA is called a chromosome.
A base is attached to the 1 position in general adenine A cytosine C guanine G or uracil U. Nucleotides perform a wide variety of functions in the living cells besides being the building blocks or monomeric units in the nucleic acid DNA and RNA structure. The bases are held together by hydrogen bonds.
Sponk Creative Commons 30 DNA deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA ribonucleic acid are the two types of nucleic acids found in. Both contain a phosphate group a sugar molecule and a nitrogenous base. The chemical formula of Uracil is C 4 H 4 N 2 O 2 and its IUPAC name is Pyrimidine-241H3H-dione.
Point Mutation Definition. In 1967 Carl Woese found the catalytic properties of RNA and speculated that the earliest forms of life relied on RNA both to carry genetic information and to catalyse biochemical reactions. A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units.
DNA is composed of a phosphate-deoxyribose sugar backbone and the nitrogenous bases adenine A guanine G cytosine C and thymine T. Three differences between DNA and RNA are that DNA uses the base thymine while RNA uses uracil DNA uses the sugar deoxyribose while RNA uses ribose and usually DNA is double-stranded and RNA is single-stranded. Whereas DNA contains deoxyribose RNA contains a different type of sugar molecule called ribose.
A uracil is a demethylated form of a thymine meaning that a methyl group CH 3 is removed from a molecule of thymine at the 5. Although RNA does not serve as the hereditary information in most cells RNA does hold this function for many viruses that do not contain DNA. Transcription is the process of producing a strand of RNA from a.
DNA and RNA are made up of many nucleotides. Although there are many nitrogenous bases the five most important to know are the bases found in DNA and RNA which are also used as energy carriers in biochemical reactions. A point mutation is a type of mutation in DNA or RNA the cells genetic material in which one single nucleotide base is added deleted or changed.
Where purines will. These include their role as structural components of some coenzymes of B-complex vitamins eg. These are adenine guanine cytosine thymine and uracil.
Like DNA RNA is a polymer of nucleotides. RNA is found both in the nucleus and the cytoplasm this way it can shuttle the DNA message from the nucleus to the targets. Adenine A Thymine T Cytosine C Guanine G The rungs of the DNA ladder are each made of two bases one base coming from each leg.
RNA is not as fragile and as such can afford to mile around in ways DNA cant. A only pairs with T and C only pairs with G. Their theories were not validated until the work of Nobel Prize laureate Thomas R.
Thus RNA clearly does have the additional capacity to serve as genetic information. The DNA stores and transfers genetic information while the RNA forms functional protein from it and its a major difference between both. Because RNA has to move around so much and performs many functions in the synthesis of proteins different types of RNA are synthesized and there is a division of labor.
Each of the nucleotides in RNA is made up of a nitrogenous base a five-carbon sugar and a phosphate group. During transcription uracil replaces the position of thymine and forms complementary pairs with adenine. Cytosine guanine adenine thymine in DNA and uracil in.
RNA consists of ribose nucleotides nitrogenous bases appended to a ribose sugar attached by phosphodiester bonds forming strands of varying. RNA abbreviation of ribonucleic acid complex compound of high molecular weight that functions in cellular protein synthesis and replaces DNA deoxyribonucleic acid as a carrier of genetic codes in some viruses. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base a pentose sugar and a phosphate.
Still it performs unique functions in other prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The phosphate groups have a negative. To make a protein the cell makes a copy of the gene using not DNA but ribonucleic acid or RNA.
The other nitrogenous bases are found in both DNA and RNA. Adenine A and thymine T can pair up because. Each nucleotide in RNA contains a ribose sugar with carbons numbered 1 through 5.
And RNA contains. Carbon residues in the pentose are numbered 1 through 5 the prime distinguishes these residues from those in the base which are numbered without using a prime notation. In the 1970s Cech was studying.
In organisms called eukaryotes DNA is found inside a special area of the cell called the nucleus. A nitrogenous base a pentose sugar and one or more phosphate groups. In the present article we.
Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base a five-carbon sugar and a phosphate group. At other times in the. However RNA as genetic material is only found in some of the viruses called retrovirus but not as our genetic material.

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
What Are The Nitrogenous Bases Of Dna And Rna Quora

What Nitrogenous Base Is Found In Rna But Not Dna Draw It To Know It
0 Comments